This article describes the direct deployment of Apache APISIX and APISIX Ingress Controller in KubeSphere using the official Apache APISIX Helm repository. And Apache APISIX can be used as a gateway or a data plane for APISIX Ingress Controller to carry business traffic.
Introduction to KubeSphere#
KubeSphere is a cloud-native application-oriented system built on top of Kubernetes, fully open source, supporting multi-cloud and multi-cluster management, providing full-stack IT automation capabilities, and simplifying enterprise DevOps workflows. Its architecture makes it easy to integrate third-party applications with cloud-native eco-components in a plug-and-play fashion.
As a full-stack, multi-tenant container platform, KubeSphere provides an operations-friendly, wizard-based interface to help organizations quickly build a powerful and feature-rich container cloud platform. DevOps, application lifecycle management, microservice governance (service grid), log query and collection, service and networking, multi-tenant management, monitoring and alerting, event and audit queries, storage management, access control, GPU support, network policies, image repository management, and security management.
Introduction to Apache APISIX#
Apache APISIX is an open source, high-performance, dynamic cloud-native gateway donated to the Apache Foundation by Shenzhen Tributary Technology Co. Apache APISIX currently covers API gateways, LB, Kubernetes Ingress, Service Mesh, and many other scenarios.
Prerequisites#
Existing Kubernetes clusters already managed in KubeSphere.
Deploy Apache APISIX and Apache APISIX Ingress Controller#
We can either enable KubeSphere's AppStore by referring to KubeSphere's documentation, or use the Helm repository using Apache APISIX (https://charts.apiseven.com) for deployment. Here, we directly use the Helm repository of Apache APISIX for deployment.
Execute the following command to add the Helm repo for Apache APISIX and complete the deployment.
➜ ~ helm repo add apisix https://charts.apiseven.com"apisix" has been added to your repositories➜ ~ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami"bitnami" has been added to your repositories➜ ~ helm repo update➜ ~ kubectl create ns apisixnamespace/apisix created➜ ~ helm install apisix apisix/apisix --set gateway.type=NodePort --set ingress-controller.enabled=true --namespace apisixW0827 18:19:58.504653 294386 warnings.go:70] apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1 CustomResourceDefinition is deprecated in v1.16+, unavailable in v1.22+; use apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 CustomResourceDefinitionNAME: apisixLAST DEPLOYED: Fri Aug 27 18:20:00 2021NAMESPACE: apisixSTATUS: deployedREVISION: 1TEST SUITE: NoneNOTES:1: Get the application URL by running these commands: export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace apisix -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services apisix-gateway) export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace apisix -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}") echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORTVerify that it has been successfully deployed and is running.
➜ ~ kubectl -n apisix get podsNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEapisix-77d7545d4d-cvdhs 1/1 Running 0 4m7sapisix-etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 4m7sapisix-etcd-1 1/1 Running 0 4m7sapisix-etcd-2 1/1 Running 0 4m7sapisix-ingress-controller-74c6b5fbdd-94ngk 1/1 Running 0 4m7sYou can see that the related Pods are running properly.
Deploying the sample project#
We use kennethreitz/httpbin as a sample project for demonstration purposes. The deployment is also done directly in KubeSphere.
Just select Services - Stateless Services and create it.
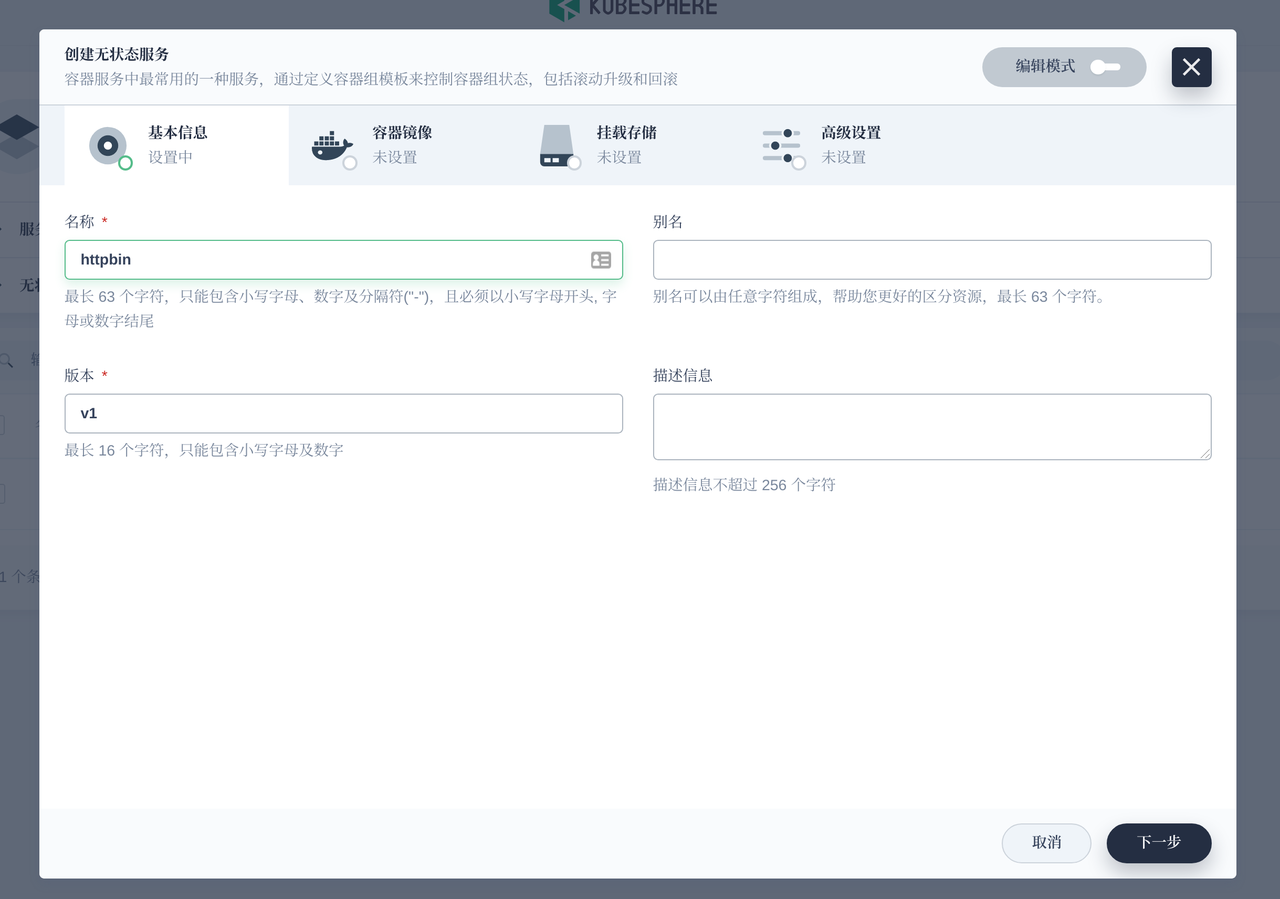
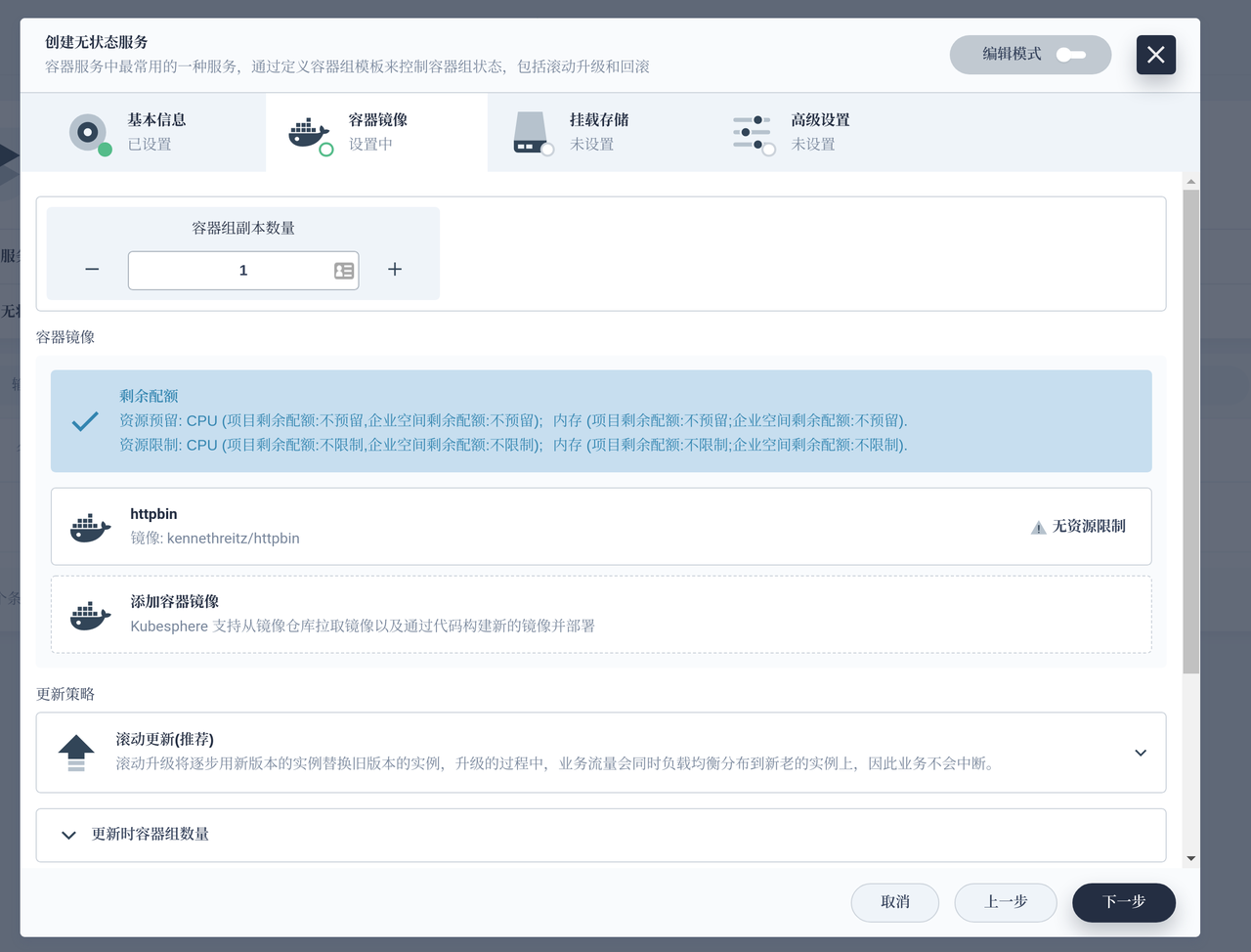
You can see the successful deployment in KubeSphere's Services and Loads interface, or you can check directly in the terminal to see if the deployment has succeeded.
~ kubectl get pods,svc -l app=httpbinNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEpod/httpbin-v1-7d6dc7d5f-5lcmg 1/1 Running 0 48s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEservice/httpbin ClusterIP 10.96.0.5 <none> 80/TCP 48sUsing Apache APISIX as a Gateway Proxy#
We start by demonstrating how to use Apache APISIX as a gateway to proxy services in a Kubernetes cluster.
root@apisix:~$ kubectl -n apisix exec -it `kubectl -n apisix get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=apisix -o name` -- bashbash-5.1# curl httpbin.default/get{ "args": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "httpbin.default", "User-Agent": "curl/7.77.0" }, "origin": "10.244.2.9", "url": "http://httpbin.default/get"}As you can see, the sample project can be accessed normally from within the Apache APISIX Pod. Next, use Apache APISIX to proxy the sample project.
Here we use curl to call the admin interface of Apache APISIX and create a route. All requests with host header httpbin.org are forwarded to the actual application service httpbin.default:80.
bash-5.1# curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1" -H "X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1" -X PUT -d '{ "uri": "/get", "host": "httpbin.org", "upstream": { "type": "roundrobin", "nodes": { "httpbin.default:80": 1 } }}'{"node":{"key":"\/apisix\/routes\/1","value":{"host":"httpbin.org","update_time":1630060883,"uri":"\/*","create_time":1630060883,"priority":0,"upstream":{"type":"roundrobin","pass_host":"pass","nodes":{"httpbin.default:80":1},"hash_on":"vars","scheme":"http"},"id":"1","status":1}},"action":"set"}You'll get output similar to the above, next verify that the proxy is successful:
bash-5.1# curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/get -H "HOST: httpbin.org"{ "args": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "curl/7.77.0", "X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbin.org" }, "origin": "127.0.0.1", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get"}The above output shows that the traffic of the example project has been proxied through Apache APISIX. Next, let's try to access the sample project outside the cluster via Apache APISIX.
root@apisix:~$ kubectl -n apisix get svc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=apisixNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEapisix-admin ClusterIP 10.96.33.97 <none> 9180/TCP 22mapisix-gateway NodePort 10.96.126.83 <none> 80:31441/TCP 22mWhen deployed using Helm chart, the Apache APISIX port is exposed by default as a NodePort. We use the Node IP + NodePort port for access testing.
root@apisix:~$ curl http://172.18.0.5:31441/get -H "HOST: httpbin.org"{ "args": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "curl/7.76.1", "X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbin.org" }, "origin": "10.244.2.1", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get"}As you can see, it is already possible to proxy services within the Kubernetes cluster outside the cluster via Apache APISIX as a gateway.
Proxy services using APISIX Ingress Controller#
We can add application routes (Ingress) directly in KubeSphere and Apache APISIX Ingress Controller will automatically sync the routing rules to Apache APISIX to complete the proxy for the service.
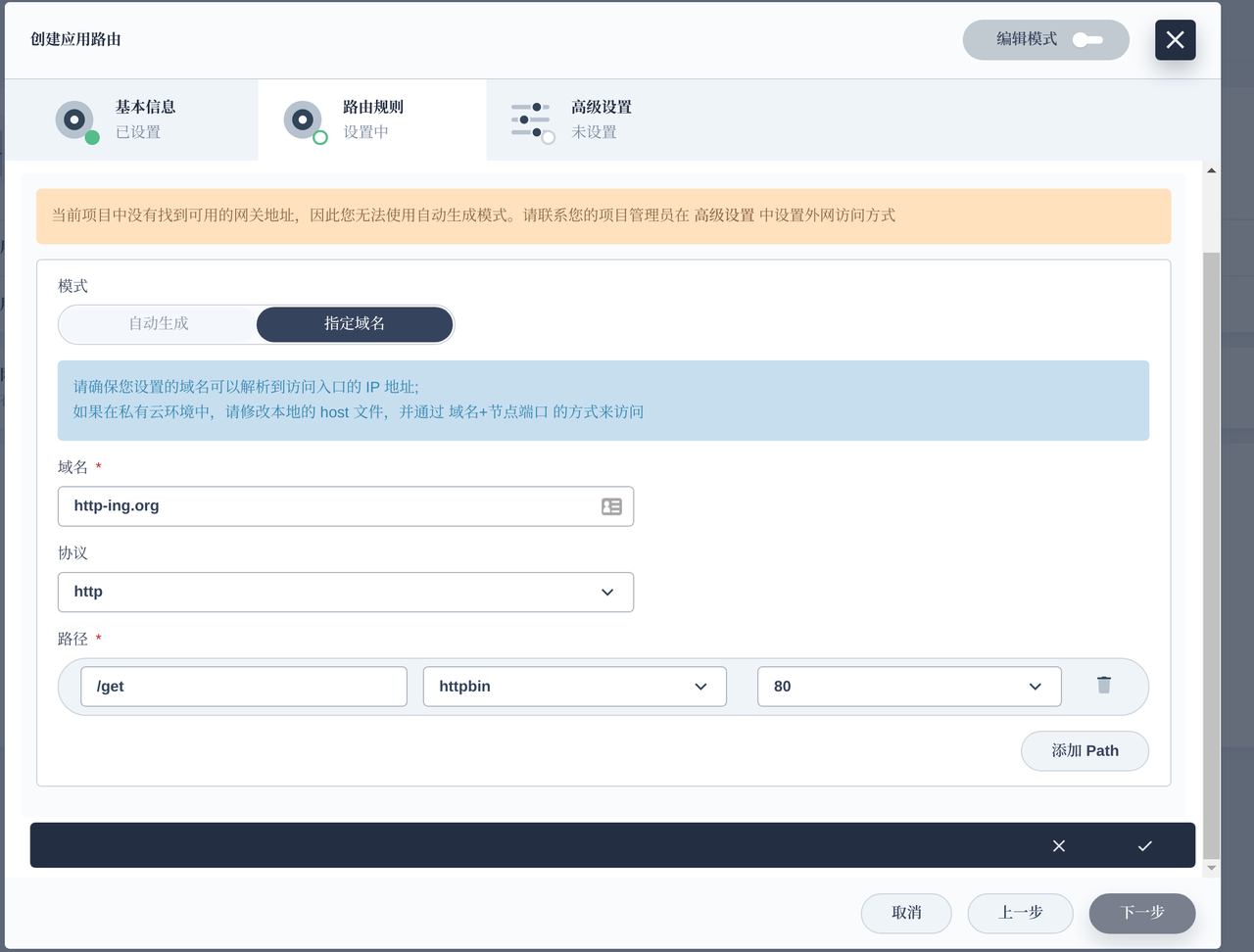
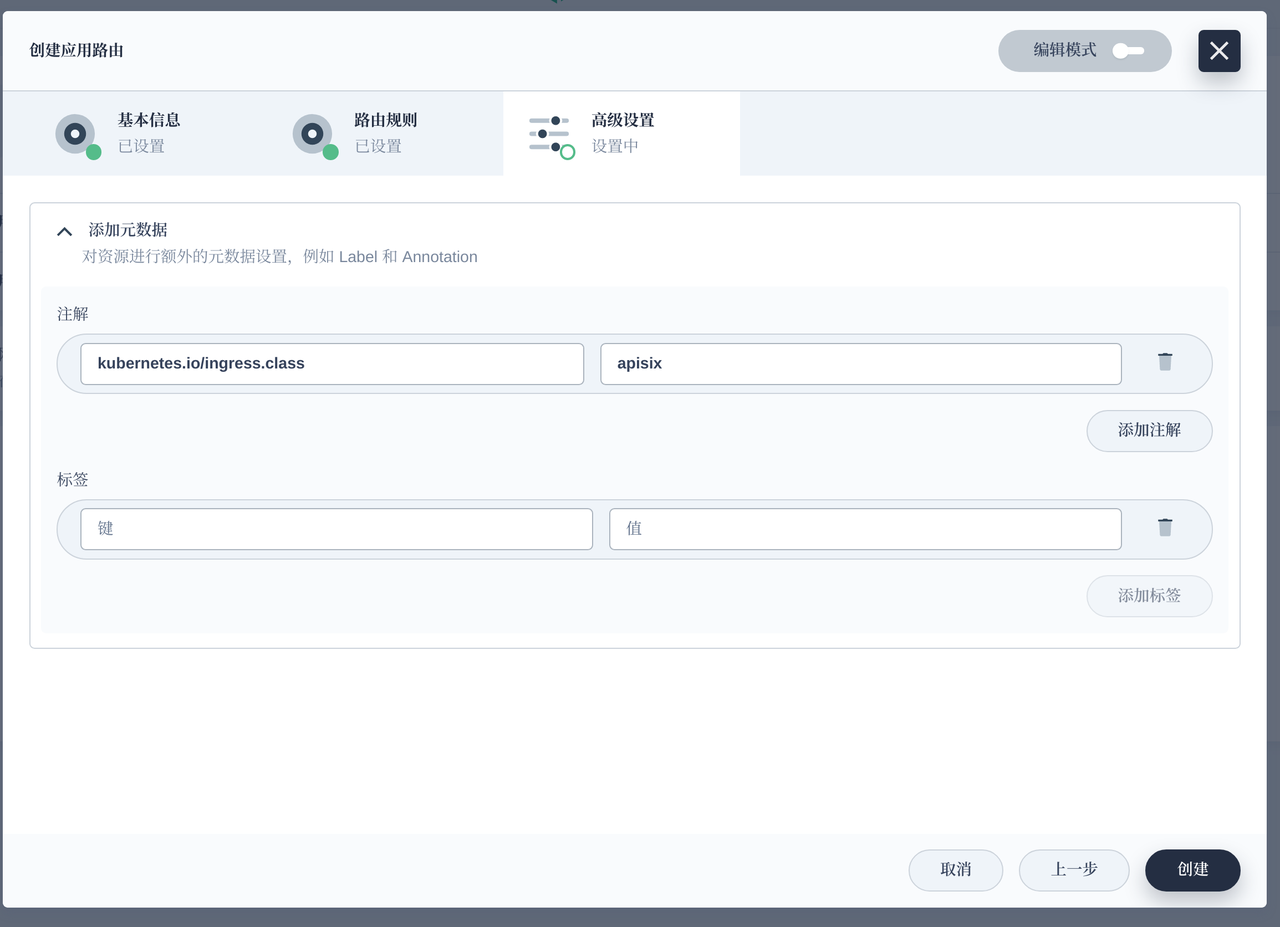
Note We added the annotation configuration of kubernetes.io/ingress.class: apisix to support multiple ingress-controller scenarios in the cluster.
After saving, you can see the following screen.
Test if the proxy is successful under the terminal.
root@apisix:~$ curl http://172.18.0.5:31441/get -H "HOST: http-ing.org" { "args": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "http-ing.org", "User-Agent": "curl/7.76.1", "X-Forwarded-Host": "http-ing.org" }, "origin": "10.244.2.1", "url": "http://http-ing.org/get"}You can see that it is also proxied properly.
In addition to the above, Apache APISIX Ingress Controller extends Kubernetes by way of CRD, and you can also publish custom resources like ApisixRoute to expose services in Kubernetes to the public.
Summary#
You can deploy Apache APISIX and APISIX Ingress Controller directly in KubeSphere using the official Apache APISIX Helm repository. And Apache APISIX can be used as a gateway or as a data plane for APISIX Ingress Controller to carry business traffic.
Future Outlook#
Apache APISIX has already partnered with the KubeSphere community, so you can find Apache APISIX directly in KubeSphere's own application repository, without having to manually add a Helm repository.